NKG Introduces H2 Combustion Firing Furnaces for Ceramics
NGK Insulators (NGK) has installed a firing furnace developed in-house for a mass production demonstration, with a view to introducing hydrogen combustion firing furnaces for actual use. NGK will develop a hydrogen burner for mass production facilities and work towards introducing it at hydrogen combustion mass production facilities. By implementing firing that does not generate carbon dioxide (CO2), NGK aims to reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 300,000 tons per year and achieve net zero CO2 emissions by 2050.
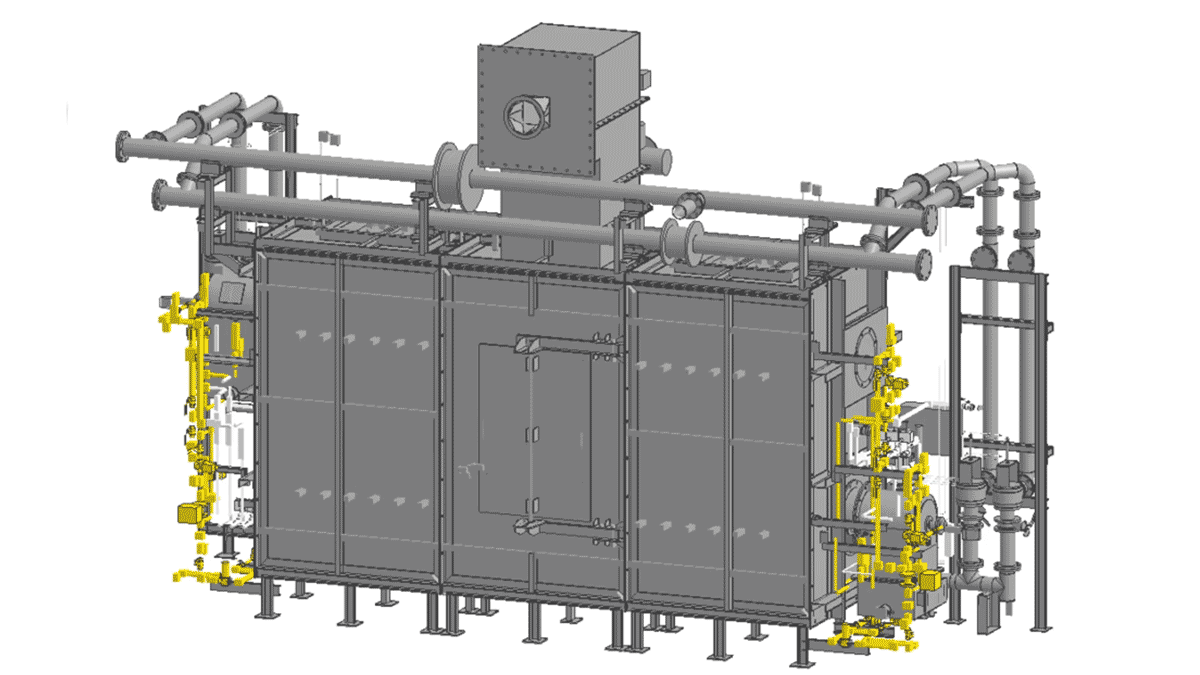
Hydrogen combustion firing furnaces for ceramics have not yet been put to practical use, but NGK has been conducting hydrogen flame evaluation tests in a test furnace installed at its headquarters area since January 2022, with the aim of developing a firing furnace with high temperatures and excellent temperature uniformity. A new firing furnace (7m wide x 2m deep x 4m high) developed by NGK will be installed at the hydrogen combustion test field located at the Technical Research Institute (in Tokai City) of Toho Gas to develop a hydrogen regenerative burner* for mass production facilities that can save approximately 50% of energy compared to conventional burners. The hydrogen combustion test field will enable burner endurance tests to be conducted at temperatures of 1,400-1,600°C, some of the highest temperatures in the firing of ceramics and will enable the evaluation and verification of high-performance ceramic products fired for long periods of time. A demonstration experiment will begin in June 2023, with the goal of establishing hydrogen combustion technology for mass production by 2025 so that it can be introduced at domestic and overseas mass production facilities from 2030.
In the NGK Group Environmental Vision, formulated in April 2021, the NGK Group has set the target of achieving net zero CO2 emissions by 2050. The group has developed its Carbon Neutrality Strategic Roadmap to realize this target, and is promoting technological innovations such as switching to non-fossil fuels in the ceramics firing process as one of its strategies to achieve this. Expertise gained from the development of hydrogen combustion will be transferred to the verification of combustion technologies using other non-fossil fuels, such as ammonia. To achieve net zero emissions by 2050, NGK will continue to promote the development of technologies that utilize clean energy in the production of ceramics and will contribute to the realization of a carbon-neutral society.
*Regenerative burner: A burner that performs both combustion and exhaust through an internal ceramic heat storing. By alternating at intervals between combustion and exhaust, the exhaust heat from the combustion gas is recovered through the heat storing and is reused to preheat the combustion air, resulting in high thermal efficiency.